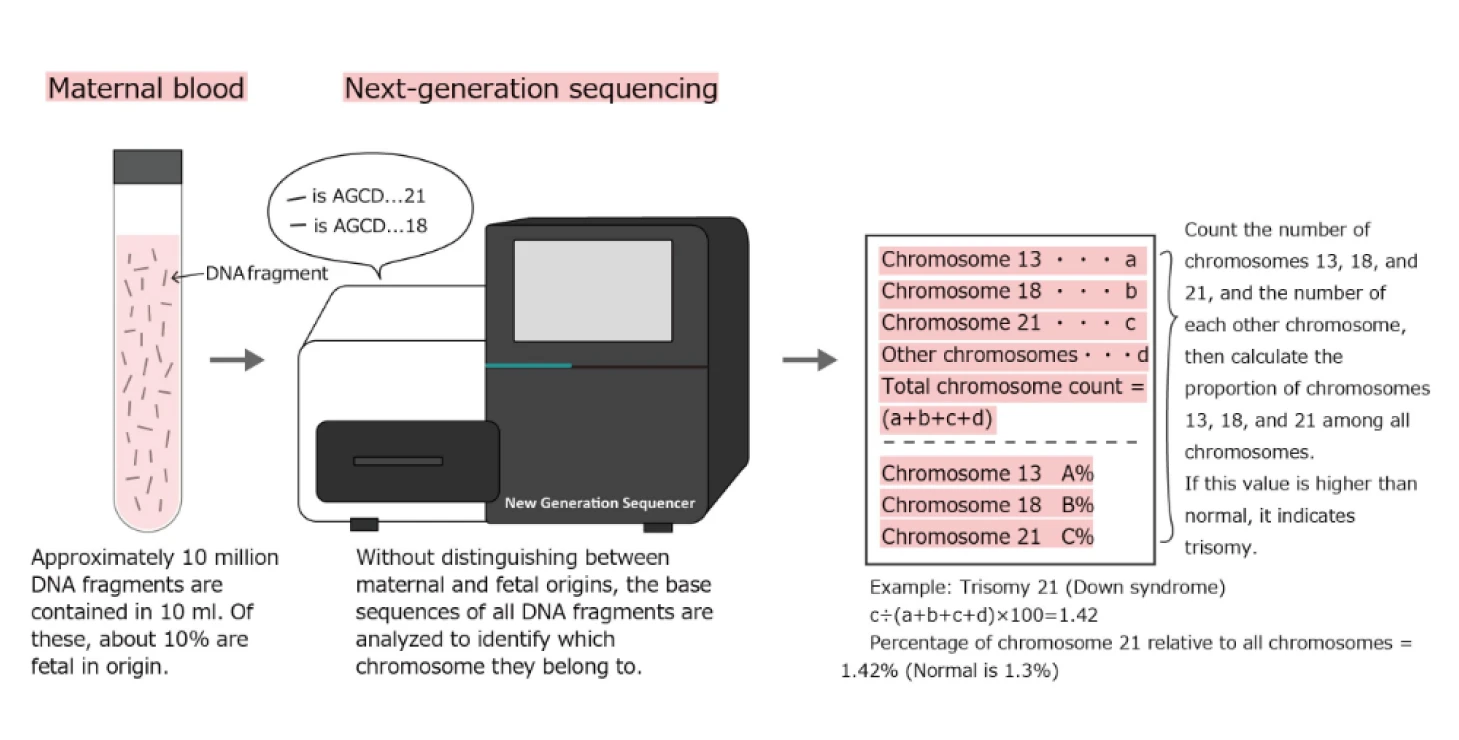
What is NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing)?
About NIPT is a test to check for numerical abnormalities in fetal chromosomes (such as trisomy 21, Down syndrome, etc.). It can be performed from the 10th week of pregnancy, earlier than amniocentesis.
In addition, the test can be performed by simply drawing blood from the arm, just like a regular blood test, and there are almost no risks associated with the test.
What can you find out?
In general, NIPT tests only for trisomies of chromosomes 13, 18, and 21. The gender of the fetus is not disclosed.
However, our NIPT can also test for gender. It is also possible to test for the number of chromosomes for all chromosomes, not just chromosomes 13, 18, and 21.
Furthermore, blood tests can be used to test for microdeletions that can cause congenital abnormalities (see the table below for detectable microdeletions).
| Type of NIPT | Test Items |
|---|---|
| NIPT LITE | Trisomy of chromosomes 13, 18, 21 and presence of Y chromosome (sex determination) |
| NIPT BASIC | In addition to NIPT LITE items, screening for aneuploidy of all chromosomes (1–22) and sex chromosome abnormalities (X, XXX, XXY, XYY) |
| NIPT PLUS | In addition to NIPT BASIC, microdeletions: 1p36 deletion syndrome (designated intractable disease 197), 2q33.1 deletion syndrome, 22q11.2 deletion syndrome / DiGeorge syndrome (designated intractable disease 203), Langer-Giedion syndrome / 8q23-24 deletion syndrome, Cri-du-chat syndrome / 5p deletion syndrome (designated intractable disease 199), Angelman/Prader-Willi syndrome / 15q11.2 deletion syndrome |
| NIPT PREMIUM | In addition to NIPT PLUS, copy number variants: partial deletion syndromes 1p, 2q, 3p25→pter, 4q21→q31, 6q, 8p deletion/duplication, 9p duplication, 10p duplication, 11q deletion/duplication, 16p duplication, 18p deletion, 20p duplication |
*Horizontal scrolling is available
Benefits & Risks
Benefits & RisksBenefits
- It is a non-invasive test
- Early testing possible
- Chorionic villus sampling (after 11 weeks of pregnancy)
- Amniocentesis (after 15 weeks of pregnancy)
- Maternal serum marker test (after 15 weeks of pregnancy)
- Combined test (after 11 weeks of pregnancy)
- High accuracy
NIPT involves taking blood from a vein in the arm and using the fetal DNA contained in the maternal blood. Therefore, unlike chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis, it is a non-invasive test with a low risk of miscarriage.
It is possible to perform the test at an earlier stage than other tests.
In addition to NIPT, genetic tests that examine chromosomes non-invasively include maternal serum marker tests (Quattro test, etc.) and combined tests that combine ultrasound marker tests and maternal serum marker tests. Both maternal serum marker tests and combined tests estimate the probability of fetal chromosomal abnormalities from changes in markers of chromosomal abnormalities (substances that indicate chromosomal abnormalities). In contrast, NIPT uses fetal DNA contained in maternal blood for testing, so it is more accurate at detecting chromosomal abnormalities than maternal serum marker tests and combined tests.
Risks
Cannot detect congenital abnormalities other than chromosomal abnormalities
Congenital abnormalities may be caused by factors other than chromosomal abnormalities. Therefore, NIPT cannot detect all congenital abnormalities. Among congenital abnormalities caused by factors other than chromosomal abnormalities that cannot be detected by NIPT, ultrasound examinations may be effective for diseases that cause morphological abnormalities.
This is a non-deterministic test
The disadvantage of NIPT is that it is a non-definitive test. The accuracy of a negative test result (no abnormality) is high, but a positive test result (abnormality) may be a false positive (a false positive that is actually negative). In that case, it is necessary to consider amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, which are definitive tests.
Methods
MethodsTesting Period
The test can be performed from the 10th week of pregnancy.
It normally takes about two weeks (maximum three weeks) from the time of blood collection for the test results to become available.
Blood Collection
As with regular blood tests, blood is generally drawn from the arm.
However, if it is difficult to draw blood from the arm, blood may be drawn from another location where it is easier to draw blood. The amount of blood drawn is approximately 10ml.